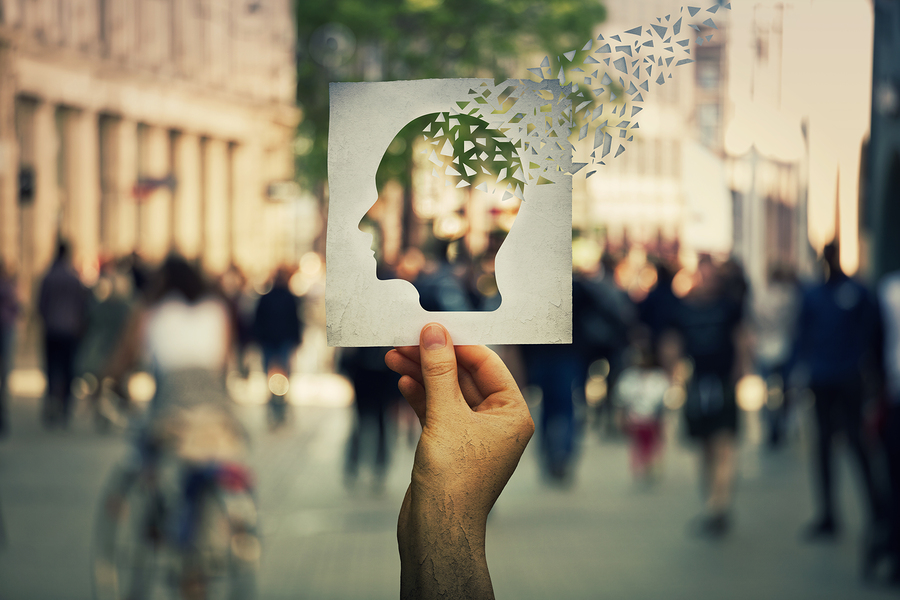
Experienced Minnesota Head Injury Lawyers serving all of Minnesota
Oftentimes car accident survivors cannot restore the quality of life they enjoyed prior to their accidents. Brain and head injuries can impair their mobility, emotional state, and ability to think. Life after a head injury presents overwhelming challenges for both the accident victim and their loved ones.

The experienced attorneys of Sand Law LLC have recovered substantial sums for Minnesota clients who have suffered head trauma due to negligent drivers. Our detailed lawyers evaluate each case from a variety of angles to ensure that clients receive maximum compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and emotional damage resulting from their accidents. We serve clients throughout Minnesota from our St. Paul, White Bear Lake, and Woodbury locations.
Traumatic Brain Injury Statistics
- Close to half a million victims of head injuries require a hospital visit yearly.
- Over 66% of head injuries are a result of automobile accidents.
- Men are twice as likely as women to suffer a head injury.
- In the United States alone, 7 million brain injuries are sustained on an annual basis.
- Almost 7% of the U.S. population currently experiences the lasting impacts of a head injury.
- Every year, roughly 50,000 fatalities in the U.S. are due to TBIs.
- Compared to those without head injuries, people with severe TBI are 2.4 times more likely to commit suicide.
Common Causes of TBIs and Head Injuries
When a driver’s head collides with an object, such as a steering wheel, it can cause blunt force trauma. Even though the head is not penetrated, the damage can be long-lasting or even fatal. This can also happen to passengers when their heads meet windshields and windows, car doors, and the seats in front of them.
Passengers and motorists can even sustain head injuries in situations where their heads make no contact with other objects. When a sudden jolt forces a person’s head to a quick stop, the brain doesn’t automatically stop with it. The brain can slam into the skull, leading to internal damage.
Bicyclists and motorcyclists commonly sustain head injuries when thrown to the pavement. Though they wear helmets as precautions, their gear isn’t an equal match for vehicles weighing thousands of pounds. Likewise, car riders who are thrust from their vehicles are also susceptible to serious brain injuries.
In an accident, virtually any object within a vehicle and its surroundings can double as a dangerous projectiles. Tree branches, personal belongings, and unsecured items from truck beds or car roofs can penetrate a human skull when they’re flung at a certain velocity. Even bone fragments from victims’ own fractured skulls can pierce into their brains.
Understanding Mild, Moderate, and Severe Brain Injuries
Traumatic brain injuries are classified into three categories: mild, moderate, or severe. Determining factors include the length of unconsciousness and/or the severity of a coma, results of brain imaging, and whether post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) occurred. Mild, moderate, and severe TBI may be characterized as follows:
Mild TBI Characteristics
Loss of consciousness – For victims of mild TBIs, the loss of consciousness is typically brief, ranging from seconds to a few minutes.
Brief post-traumatic amnesia – Affected people may be unable to recall basic information like their names and the date for up to an hour following an accident. Their memory of the accident can also be foggy.
Normal brain imaging results – CT scans and MRIs often produce normal results when a mild TBI is present, so it is important to describe your condition to a doctor.
Moderate TBI Characteristics
One to 24 hours of unconsciousness – Brain swelling and limited blood flow are two factors that can make moderate TBI victims lose consciousness for up to 24 hours.
PTA lasting for up to 24 hours – PTA lasting between one and 24 hours is a sign that a TBI may be moderate rather than mild. Patients may continue to feel confused for a few days or weeks as well.
Abnormal brain imaging results – While moderate TBIs can remain undetected in imaging results, brain imaging often does reveal lesions and other signs of damage.
Severe TBI Characteristics
Unconsciousness or coma for over 24 hours – Oxygen deprivation, brain swelling, and bleeding are some factors that can leave a patient in a comatose state. A coma can also be a sign that the brain is taking time to attempt repairing itself.
PTA for more than 24 hours – Those who endure PTA for over 24 hours are likely to have a severe TBI that can result in long-lasting or permanent impairments.
Abnormal brain imaging results – In addition to lesions, brain imaging results may reveal the loss of white matter connectivity, a condition that causes nerve damage.
Other Types of Brain Injury Severities
Coma – It is important to seek medical attention immediately when someone is unconscious. Comas require quick intervention to save a person’s brain function and life.
Vegetative State – Patients in a vegetative state are awake but do not meaningfully respond to their environment.
Persistent Vegetative State – When patients remain vegetative for over a month, their condition is labeled as a persistent vegetative state. It is most often irreversible.
Minimally Responsive State – Patients in a minimally responsive state show some signs of awareness such as making eye contact, gesturing, and giving simple verbal responses. These interactions may be inconsistent.
Consequences of Mild, Moderate, and Severe TBIs
Mild TBI
People who have sustained mild TBIs may face problems processing information as quickly as they did prior to their brain injury. Mild TBIs can also diminish their ability to concentrate which can increase the time it takes to complete tasks.
Those with mild TBIs may notice that their short-term memory fails them when it comes to abilities like recalling details of a conversation or remembering to return a phone call.
Mild TBIs can make it difficult to control emotions. Affected individuals may find themselves more easily upset or anxious over annoyances they would typically overlook.
Mild TBIs can leave people feeling sluggish, nauseous, and dizzy. Understandably, migraines and persistent headaches are common complaints of mild TBI patients.
Moderate and Severe TBI
Reduced ability to process and remember information, concentrate, and overcome challenges can make TBI sufferers feel frequently frustrated. Additionally, TBI patients may struggle to stay organized and solve problems as efficiently as they used to. Consequently, returning to their normal work load sometimes isn’t possible.
Those who suffer from moderate or severe TBI may have trouble controlling their emotions, including anger. They may become verbally or physically aggressive over just a slight provocation. In some cases, they lack the motivation they once had to fulfill their responsibilities and can even become apathetic toward their personal interests.
Loved ones may notice that a TBI patient develops a childlike dependence on them for tasks that were once done independently. With so many new difficulties, it is no surprise that many TBI victims suffer from depression.
Both moderate and severe TBIs can impair a person’s senses. Those with a TBI may experience blurred vision and can even partially or completely lose their sight. Ear damage can manifest as a loss of hearing or an increased sensitivity to sound. Tinnitus, which is ringing in the ears, also presents itself in some TBI patients.
Moderate or severe TBIs can cause chronic pain in virtually in area of the body. Various parts of the body may not function as reliably as they once did. For example, those with severe TBIs can face difficulties with speaking as well as controlling bowel and bladder movements. In some of the worst cases, brain damage can leave victims partially or fully paralyzed.
Types of Traumatic Brain Injuries
Concussion – A person with a concussion may experience nausea or vomiting, headaches, and memory loss.
Contusion – A bruise in brain tissue is caused by broken or damaged blood vessels.
Coup-Contrecoup – This term describes an injury that begins at the site of trauma and also occurs at the opposite side of the brain.
Diffuse Axonal Injury – DAIs cover a large surface. Numerous lesions present in both gray and white matter of the brain.
Penetration – Penetrative damage is exponentially more likely to be fatal when projectiles make contact at a high velocity.
Hematoma or Blood Clot – When a blood vessel near the brain’s surface bursts, a life-threatening pool of blood known as a hematoma can form.

Contact a Minnesota Traumatic Brain Injury Lawyer Today
Sand Law attorneys have represented numerous clients who have sustained brain injuries. We understand that this is a difficult process to face alone. If you have suffered head trauma due to another party’s negligence, speak with one of our personal injury lawyers today. Contact us at 651-291-7263 or fill out our contact form for a free consultation.